Export Essentials
While many regulations may affect exports, we focus on those that are most typical for ECU activities here.
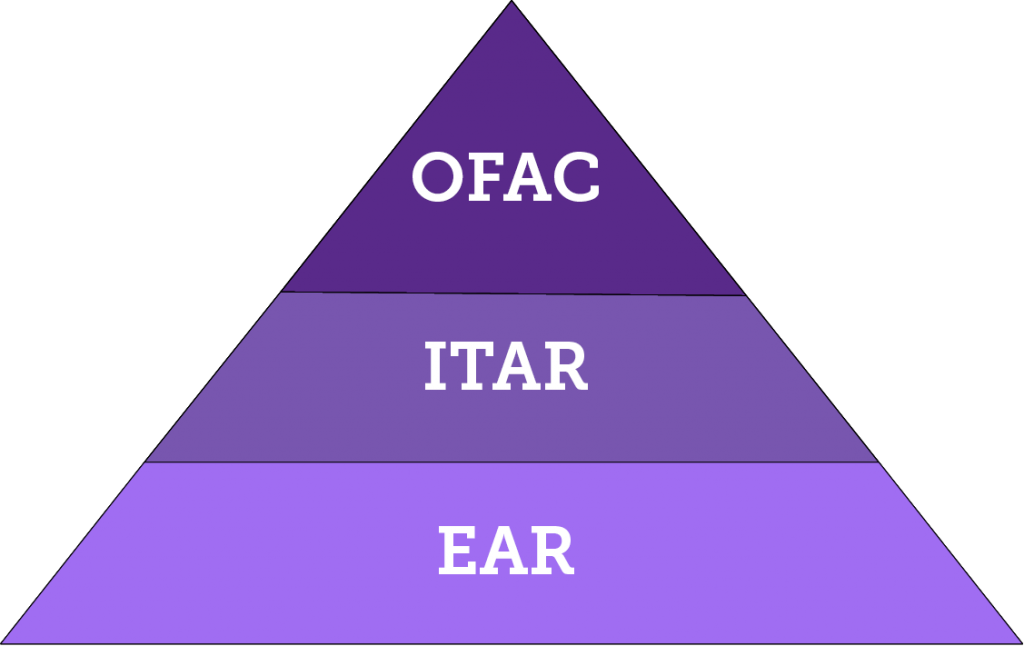
OFAC – U.S. Office of Foreign Assets Control, Department of Treasury
Think of OFAC’s regulations as top-level restrictions or prohibitions, also known as sanctions, that can prohibit engaging in activities with not only certain countries, but also with specific individuals, regardless of country, because of the individual’s role in some undesired activity.
- Country Example: The U.S. views various policies of the government of Syria as a threat to U.S. national security, foreign policy and to the economy. Thus, one of the most comprehensive set of sanctions exists for interactions with Syria. Highly-sanctioned countries include Cuba, Iran, North Korea and Syria.
- Individual Example: The U.S. views narcotics trafficking as a threat to national security, foreign policy and to the economy. Engaging in activities with individual Colombian narcotics traffickers and narcotics-related organizations are prohibited.

ITAR – International Traffic in Arms Regulations, Department of State
ITAR focuses on regulating defense articles and services. Whereas OFAC sanctions are broad in the sense that any engagement in certain activities might be restricted, ITAR regulates only defense-related activities. If you’re working on research for an item that, for example, will be incorporated into a military missile, ITAR might restrict who can have access to design drawings or where we can ship prototypes.
ITAR Examples
| ITAR Categories of Items/Technology and Information/Software Controlled | Examples |
|---|---|
| Category I: Firearms, close assault weapons and combat shotguns | Combat shotguns, rifles, revolvers, submachine guns, technical data for some firearms |
| Category II: Guns and armament | Flame throwers, tooling and equipment and test models, target acquisition or damage assessment systems |
| Category III: Ammunition/ordnance | Ammunition handling equipment, technical data and defense services |
| Category IV: Launch vehicles, guided missiles, ballistic missiles, rockets, torpedoes, bombs and mines | Rockets, bombs, torpedoes and hand grenades |
| Category V: Explosives and energetic materials, propellants, incendiary agents and their constituents | Explosives, zirconium (CAS 7440-67-7), magnesium (CAS 7439-95-4), or alloys of these and lead salicylate (CAS 15748-73-9) |
| Category VI: Surface vessels of war and special naval equipment | Firing lasers and missiles |
| Category VII: Ground vehicles | Software related to defense articles and rotary shock absorbers for vehicles weighing more than 30 tons |
| Category VIII: Aircraft and related articles | Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), attack helicopters and target drones |
| Category IX: Military training equipment and training | Training equipment for ground targets and missile launch trainers |
| Category X: Personal protective equipment | Body armor and parts and components for personal protective equipment |
| Category XI: Military electronics | Electronic equipment with underwater hardware, equipment with active or passive acoustic array sensing systems or acoustic array equipment capable of real-time processing that survey, detect and track, localize or identify, surface vessels, submarines, other undersea vehicles, having multi-static capability or operating frequency less than 20 kHz or operating bandwidth greater than 10kHz |
| Category XII: Fire control, lasers, imaging and guidance equipment | Developmental lasers funded by the Department of Defense via contract or other funding authorization and imaging systems |
| Category XIII: Materials and miscellaneous articles | Military or intelligence cryptographic (including key management) systems, equipment, assemblies, modules, integrated circuits, components and software (including their cryptographic interfaces) capable of maintaining secrecy or confidentiality of information or information systems, including equipment or software for tracking, telemetry and control (TT&C) encryption and decryption, non-transparent ceramic plate or blanks greater than 1⁄4 inches thick and larger than 8 inches × 8 inches for transparent armor, including spinel and aluminum oxynitride (ALON), biological agents such as Bacillus anthracis, Ebola virus, Variola major virus (Smallpox virus) and AB-G-BRU-A Goat anti-Brucella abortus |
| Category XV: Spacecraft and related articles | Spacecraft, including satellites and space vehicles, whether designated developmental, experimental, research or scientific, or having a commercial, civil or military end-use, that are specially designed to mitigate effects (e.g. scintillation) of or for detection of a nuclear detonation |
| Category XVI: Nuclear weapons related articles | Modeling or simulation tools that model or simulate the environments generated by nuclear detonations or the effects of these environments on systems, subsystems, components, structures or humans. |
| Category XVIII: Directed energy weapons | Directed energy weapons that cause ocular disruption or blindness |
| Category XIX: Gas turbine engines and associated equipment | Turbofan and Turbojet engines (including those that are technology demonstrators, developmental engines or variable cycle engines) capable of 15,000 lbf (66.7 kN) of thrust or greater |
| Category XX: Submersible vessels and related articles | Submarines specially designed for military use |
| Category XXI: Articles, technical data and defense services not otherwise enumerated | Any article not enumerated on the U.S. Munitions List |

EAR – Export Administration Regulations, Department of Commerce
EAR has a broader scope than ITAR. For example, nearly any physical shipment is subject to EAR and various levels of controls exist depending on the item or activity, the destination and the intended end use. Despite being subject to EAR, an item might not require any license. On the other hand, an item might require a license only to certain destinations. The item might also require a license if it is intended to be used in a specific way.
EAR Examples
| EAR Categories of Items/Technology and Information/Software Controlled | Examples |
|---|---|
| Category 0: Nuclear materials, facilities and equipment and miscellaneous items | Specially designed components and parts for ammunition, shotguns with barrel length 18 inches (45.72 cm) or over, oil and gas exploration equipment, software and data |
| Category 1: Special materials and related equipment, chemicals, microorganisms and toxins | Fingerprinting powders, dyes and inks, pumps capable of circulating solutions of concentrated or dilute potassium amide catalyst in liquid ammonia (KNH2/NH3), human and animal pathogens and toxins such as Brucella abortus and Cholera toxin |
| Category 2: Materials processing | Portable electric generators and specially designed parts and components, vibration test systems, motion simulators, biocontainment chambers, isolators or biological safety cabinets |
| Category 3: Electronics | Certain analog-to-digital converter microcircuits, frequency changes (converters or inverters), high-power or high-voltage direct current power supplies, mass spectrometers, automated fingerprint retrieval systems, photo-optical step and repeat cameras |
| Category 4: Computers | Digital computers and software |
| Category 5: Telecommunications and information security | Telecommunication systems and equipment designed for being underwater, telecontrol equipment modified for unmanned aerial vehicles (including drones), information security equipment modified to perform cryptanalytic functions (functions designed to defeat cryptographic mechanisms in order to derive confidential variables or sensitive data, including clear text, passwords or cryptographic keys) |
| Category 6: Sensors and lasers | Certain Side Scan Sonar (SSS) or Synthetic Aperture Sonar (SAS) designed for seabed imaging, specially designed transmitting and receiving acoustic arrays and designed or modified to operate at depths exceeding 500 meters, and an “area coverage rate” greater than 750 m2/s while operating at the maximum range with “along track resolution” less than 15 c.m., and “across track resolution” less than 15 c.m., magnetometers, high-speed cameras, imaging devices and carbon dioxide lasers with a CW output power > 10 kW |
| Category 7: Navigation and avionics | Linear accelerometers, gyros specified to function at acceleration levels less than or equal to 100 g, Galileo Global Navigation Satellite Systems |
| Category 8: Marine | Underwater camera equipment |
| Category 9: Aerospace and propulsion | Marine gas turbine engines, resin impregnated fiber prepregs and metal coated fiber preforms |
Other Regulations with Reporting and Recordkeeping Requirements
While OFAC regulations, ITAR, and EAR are the primary purview of export controls, other U.S. agencies sometimes have requirements for the physical movement of goods, including samples and specimens used in research activities. These include:
- APHIS – Animal Plant Health Inspection Service
- Census – U.S. Census Reporting
- DEA – U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency
- FWS – U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
- Recordkeeping
- TSCA – U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s Toxic Substances Control Act